Types Of Incontinence
Fecal Incontinence
6 Jul, 2011
Fecal Incontinence
What is fecal incontinence?
Also called bowel incontinence, fecal incontinence is the loss of bowel control that results in unexpected passage of stool. While living with this condition can feel socially isolating, improving diet and getting some daily exercise can help manage it.Fecal incontinence causes
Fecal or bowel incontinence is often caused by one or more of the following:- Constipation – this is the biggest cause of loss of bowel control in the elderly.
- Diarrhea, due to chronic diseases of the bowel, such as Crohn’s diseases, diverticulitis, or inflammatory bowel disease. It could also be due to medications, radiotherapy, alcohol, infection or some food allergies.
- Social and mobility issues such as inability to reach the toilet due to poor mobility, cognitive deficit or poor communication skills.
- Neurological Impairment associated with neurological diseases such as Stroke, Multiple Sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease. The nerve supply to the bowel can also be damaged due to Diabetes, spinal cord injuries, tumors or radiation therapy.
- Structural sphincter damage following injury, surgery or complicated childbirth.
- Other causes may include Cancer, Rectal prolapse, Anal Fissure or Hemorrhoids.
Fecal incontinence treatment
Dietary & lifestyle changes
Improving regularity by eating a healthy diet, drinking enough water and participating in regular exercise can make a big difference in helping to improve bowel control. You may also need to look at mobility issues and make sure there is easy access to the toilet and sufficient privacy.Medication, therapies & surgeries
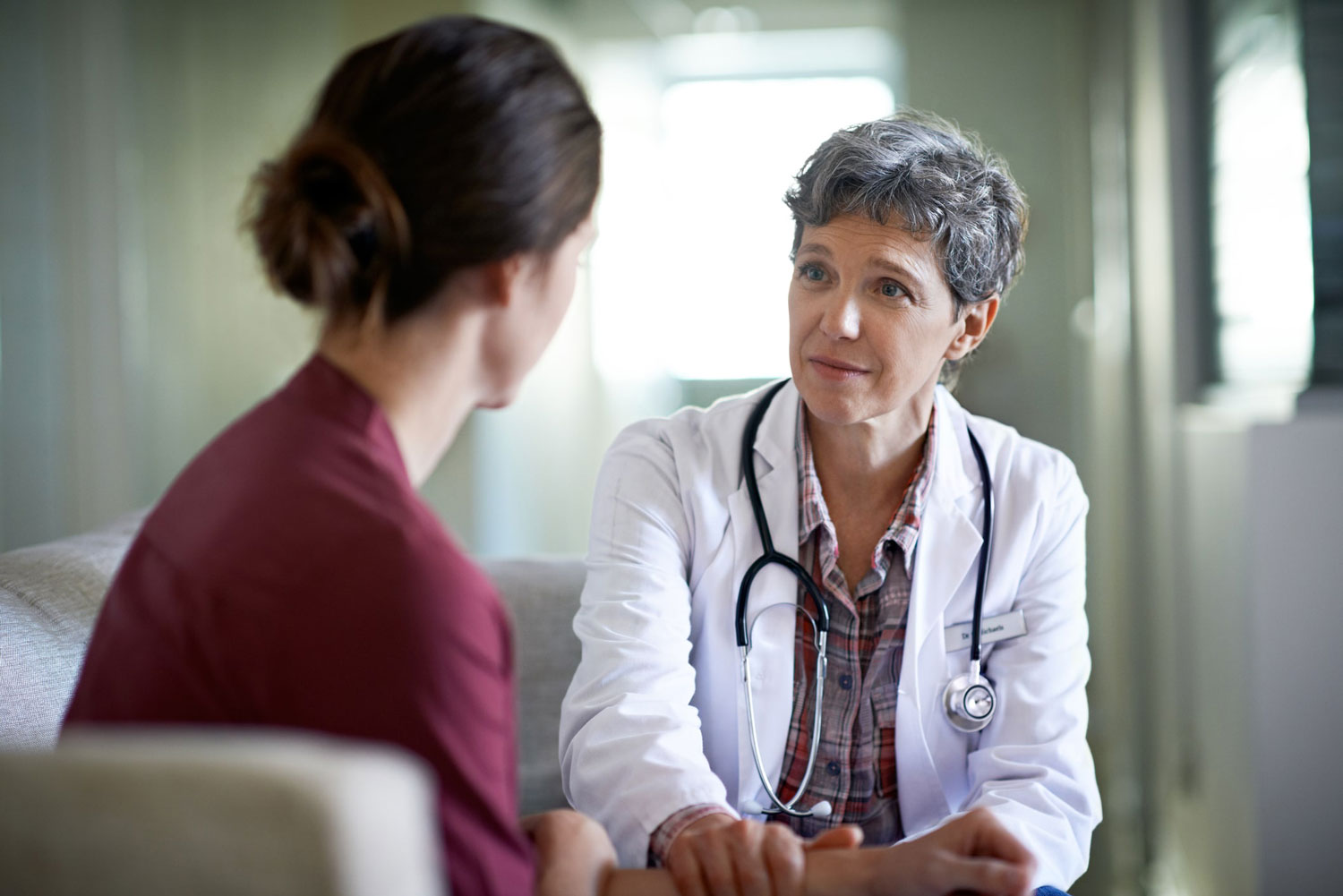
Talk to your doctor or healthcare professional about your situation, because in many cases bowel incontinence can be managed and the solutions may differ depending on the causes.
Kimberly-Clark Canada makes no warranties or representations regarding the completeness or accuracy of the information. This information should be used only as a guide and should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional medical or other health professional advice.